Auditing with Ranger
Auditing with Apache Ranger enables ArcEngine to log user access events on database objects. Apache Ranger is the designated Hortonworks Data Platform authorization provider.
Arcadia Enterprise supports full Ranger auditing, logging authorization requests that include details about time of attempt, user, client IP, the access level requested, the target object of the request, and if it was allowed or denied. It does not show the actual statement that generates these access requests. Ranger auditing also supports multiple log destination types, such as Solr, HDFS, and database.
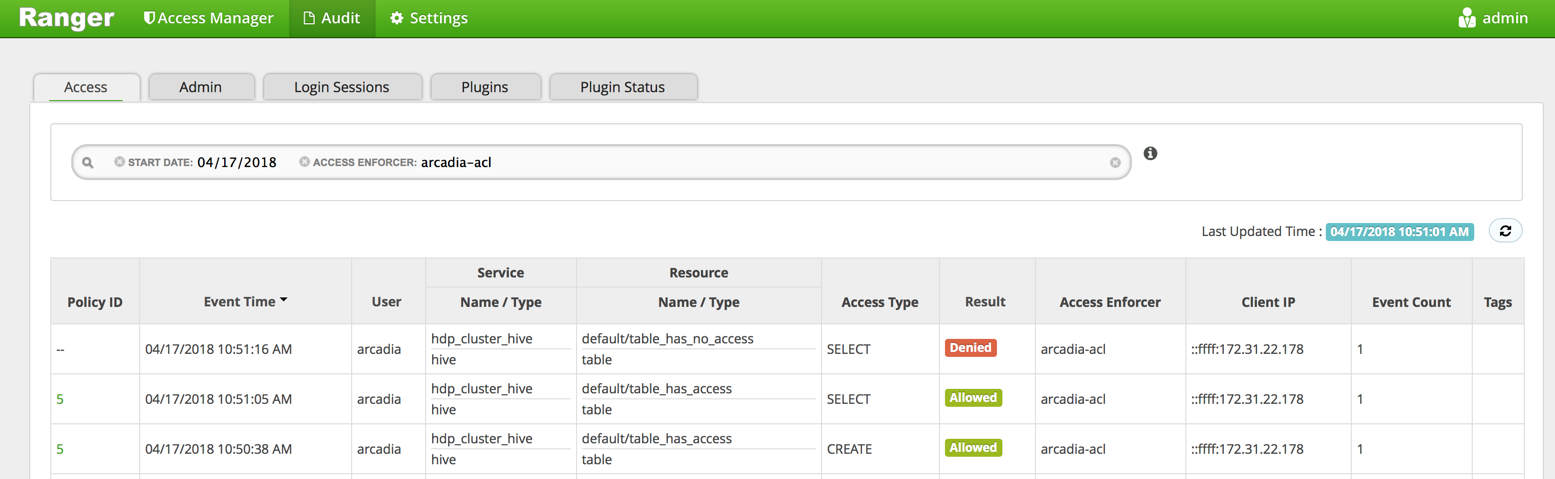
Because ArcEngine uses the same policies as Hive, Apache Ranger logs ArcEngine access events under the Hive service. To determine which events originate with ArcEngine and which originate with Hive, examine the Access Enforcer field of the audit log:
The
arcadia-aclaccess enforcer logs ArcEngine events.
The
ranger-aclaccess enforcer logs Hive events.
Integration
ArcEngine integrates with the Ranger audit ecosystem through the Ranger API, using Ranger
plug-ins to provide audit handlers. ArcEngine uses the standard Ranger audit configuration
file, ranger-arcengine-audit.xml. The resulting ArcEngine audit logs appear
under the Hive service, with an access enforcer set to arcadia-acl.
ArcEngine's Ranger audit capability attempts to match Hive Ranger audit logs for similar
statements. For ArcEngine-only statements, ArcEngine logs the access events necessary to
complete the statement. For example, when the user runs REFRESH ANALYTICAL
VIEW, ArcEngine generates access events for ALL privilege on
the analytical view, and for SELECT privilege on the base table.
Target Object Identification
ArcEngine generates audit logs based on the objects referenced directly in a user-supplied statement. Consider these examples:
If a user runs the following statement:
SELECT max(i) FROM test_table;and it is re-written to use an analytical view:
SELECT max_finalize(c1) FROM test_table_av;Then the audit log only shows access on the table
test_table.-
If the originating statement selects directly from the analytical view:
SELECT max_finalize (c1) FROM test_table_av;Then the audit log shows access to
test_table_av, because the statement references the analytical view in the original query that the user provides. If a user performs operations directly on the analytical view:
DROP ANALYTICAL VIEW test_table_av;Then the audit log shows that the
DROPis againsttest_table_av, even though the authorization check is actually againsttest_table.
Differences Between Hive and ArcEngine Logging
The current known differences between Hive and ArcEngine Ranger Audit messages include the following:
- ArcEngine does not log
SHOW DATABASEaudit logs. - ArcEngine logs
CREATE/UPDATEnew table andSELECT (base-table)for a CTAS. Hive logs only aCREATEon the new table, and aSELECTfrom the base table. - ArcEngine only logs the
DROPon database forDROP DATABASE db_name CASCADE. Hive logs aDROPfor each sub-object.
This image contrasts the appearance of the Hive and ArcEngine audit log entries, in that order:
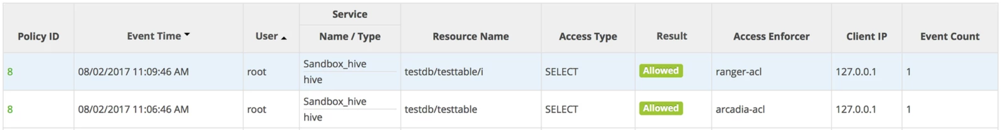
Comparison of ranger-acl and arcadia-acl audit entries
Installation
The installer correctly configures Ranger auditing and authorization in most default
settings. In cases where the default configuration does not work, the Ambari configuration
panes let us modify the two configuration files,
ranger-arcengine-security.xml and
ranger-arcengine-audit.xml.
You can enable Apache Ranger when installing or upgrading Arcadia Enterprise through Ambari Stacks.
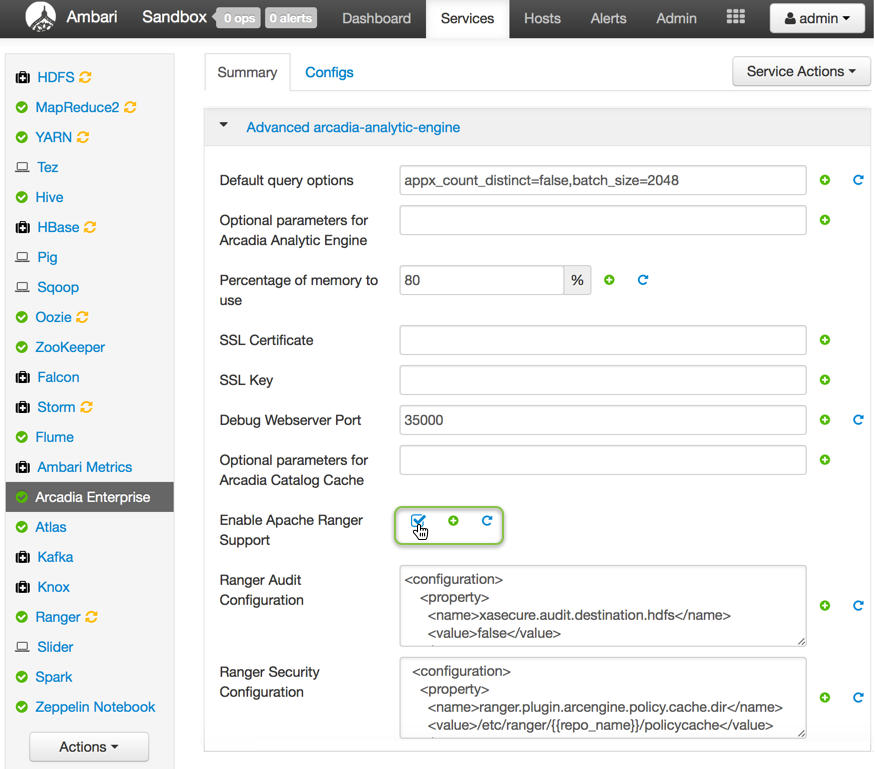
Configuration
Ambari Stacks configures Arcadia Enterprise
through the Advanced arcadia-analytic-engine configuration. Search for the field
Ranger Audit Configuration field; it contains the
ranger-arcengine-audit.xml file that configures the audit plugin.
Enabling Auditing
ranger-arcengine-audit.xml file, change the value of
xasecure.audit.is.enabled to
true:<property>
<name>xasecure.audit.is.enabled</name>
<value>False</value>
</property>For Solr logging, change xasecure.audit.destination.solr to
true:
<property>
<name>xasecure.audit.destination.solr</name>
<value>True</value>
</property>For HDFS logging, change xasecure.audit.destination.hdfs to
true; note that an Arcadia user must have WRITE
permissions in HDFS for the Ranger audit directory. By default, it is
/ranger/audit.
<property>
<name>xasecure.audit.destination.hdfs</name>
<value>True</value>
</property>You can find additional information on Apache Ranger Audit Configuration.
Limitations
- Arcadia Enterprise does not support auditing on a kerberized Solr instance.
- Apache Ranger does not log
SHOW TABLESorSHOW DATABASESevents.